From 2015 to 2025, China's commercial aerospace industry has made an astonishing leap from "starting" to "starting". The industrial scale has achieved a significant increase, from over 300 billion yuan in 2015 to over 2.3 trillion yuan in 2024, tripling in ten years; The number of commercial launches has surged from zero to 33 in 2024, accounting for nearly 50% of the total number of space launches that year; In terms of the number of enterprises, a diversified and competitive industrial ecosystem has been formed. In 2024 alone, there were over 10000 registered commercial aerospace related enterprises, and the current total number of registered enterprises exceeds 80000; From the market access policy ten years ago to its first inclusion in the government work report in 2024, driven by top-level design and policy implementation, commercial aerospace has become a new engine of global economic growth and a new focus of great power competition.
The turning point of any industry does not come overnight. Behind it is an evolutionary path full of breakthroughs, controversies, coldness, and prosperity. TIC attempts to reconstruct the true path of China's commercial aerospace industry from "single point breakthrough" to "system transition" by sorting out ten key events between 2015 and 2025, providing a reference development coordinate system for the industry; I also hope to use concrete events and data to help more people understand how China's commercial aerospace industry has gradually empowered various industries and entered consumer life from an unattainable cutting-edge project, so as to personally perceive the surging power of hard technology innovation.
01
2015: Policy Breaks Ice, Opening the Door to Commercial Aerospace Access
2015 is a milestone year in the history of China's commercial aerospace development. On October 29th, the "National Medium - and Long Term Development Plan for Civil Space Infrastructure (2015-2025)" was released, which guides the exploration of new mechanisms for market-oriented and commercialized development of national civil space infrastructure, supports and guides social capital to participate in the construction and application development of national civil space infrastructure, actively carries out comprehensive application demonstrations of remote sensing, communication, navigation at multiple levels such as regional, industrial, international, and technological development, and provides policy support for private enterprises to participate in core links such as launch, satellite manufacturing, and operation. Commercial aerospace has officially broken the ice in China, and the first batch of private aerospace startups have emerged, officially opening up a new industrial ecosystem of "national team leadership and private enterprise collaboration".

Notice on Issuing the National Medium - and Long Term Development Plan for Civil Space Infrastructure (2015-2025)
02
October 2015: "Jilin-1" was launched, pioneering the application of commercial satellites in China
At 12:13 on October 7, 2015, the first batch of four satellites in the "Jilin-1" optical remote sensing satellite constellation were successfully launched into a sun synchronous orbit at an altitude of 650 kilometers at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center. This is not only the first large-scale launch of a private satellite enterprise in China, but also the first commercial high-resolution remote sensing satellite, Jilin-1 Optical A Satellite, which has wide application value in fields such as land survey, urban planning, agricultural and forestry resource management, and disaster prevention and reduction. It provides a replicable practical model for the market-oriented operation of commercial satellites in China.
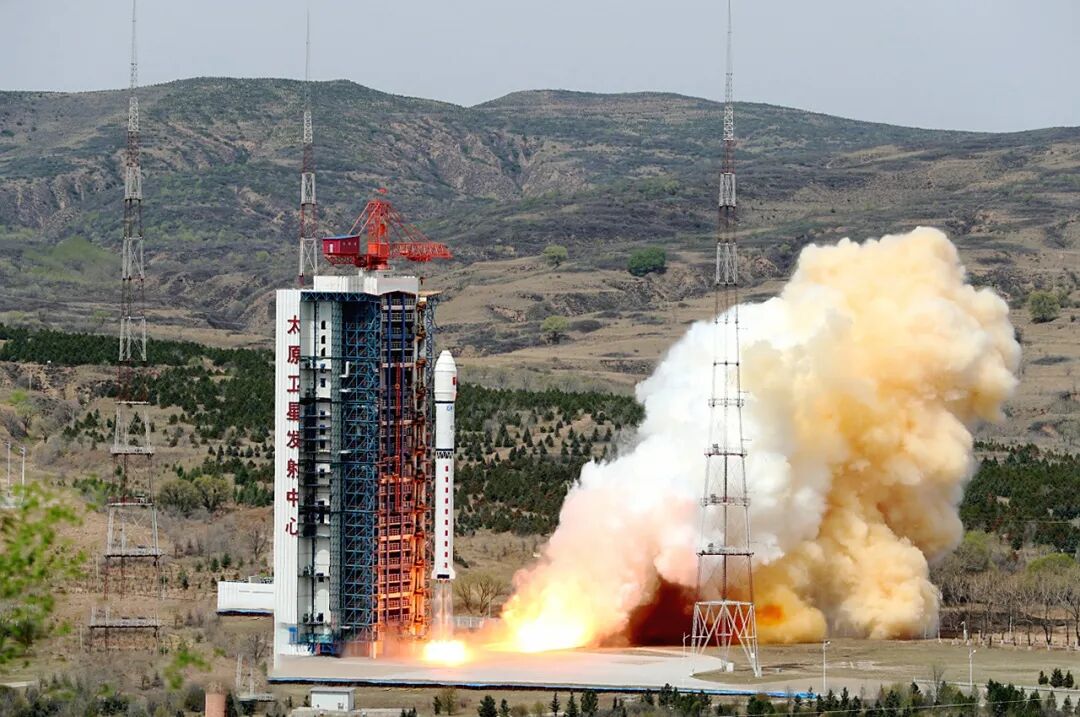

Jilin-1 successfully launched a four-star rocket from Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center
03
July 2019: "Hyperbolic One" entered orbit, achieving a "zero breakthrough" for private rockets
At 13:00 on July 25, 2019, the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center received good news: the private carrier rocket "Hyperbolic One" developed by Star Glory was successfully launched, accurately sending two satellites and multiple payloads into the predetermined 300 kilometer circular orbit according to the flight schedule. This is a key breakthrough for China's private carrier rockets to achieve "from suborbital flight to low Earth orbit" for the first time. "Hyperbolic One" breaks the monopoly of state-owned rockets on the launch market, marking the official transition of China's commercial aerospace from the "technological exploration stage" to the "commercial operation stage", and instantly ignites the capital market's enthusiasm for the commercial rocket track.

Launch image of "Hyperbolic No.1"
04
July 2020: "Beidou-3" opened, laying a solid foundation for commercial aerospace "time and space base"
On July 31, 2020, the Beidou-3 global satellite navigation system was officially launched, marking the decisive victory of Beidou's "three-step" development strategy. The Beidou system consists of 24 medium Earth orbit satellites, 3 geostationary orbit satellites, and 3 inclined geosynchronous orbit satellites, totaling 30 satellites. The completion of Beidou-3 is not only a milestone in China's satellite navigation industry, but also fundamentally builds a time-space infrastructure base for commercial aerospace, provides core support for subsequent application scenarios such as commercial satellite Internet, UAV logistics, intelligent driving, etc., and also lays a system foundation and international reputation for China's satellite navigation technology going to sea and serving the world.
Schematic diagram of Beidou-3 global satellite navigation system
05
July 2023: Liquid oxygen methane rocket enters orbit, breaking foreign 'technological monopoly'
At 9:00 am on July 12, 2023, the "Zhuque-2" Yao-2 liquid oxygen methane carrier rocket developed by Blue Arrow Aerospace successfully launched a satellite into orbit at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, becoming the world's first liquid oxygen methane carrier rocket to successfully enter orbit. This marks a revolutionary breakthrough in the application of new propellants in China's commercial aerospace industry and completely breaks the monopoly of foreign countries in this technology field. The success of the liquid oxygen methane rocket not only reduced the commercial launch cost by more than 30%, but also solved the bottleneck of the delivery cost of large-scale satellite Internet networking, providing a low-cost solution for the commercial deployment of LEO satellite constellations.

Picture of the transportation of the "Zhuque-2" Yao-2 liquid oxygen methane carrier rocket
06
September 2023: "Mobile phone directly connected to satellite", connecting the "last mile" of satellite consumer applications
On September 3, 2023, Huawei Mate60Pro will be fully available for sale, and one of its core highlights is the support for communication through the "Tiantong-1" satellite - users can connect to geostationary orbit satellites 36000 kilometers away from Earth in areas without ground signal coverage, enabling high-definition voice calls and SMS sending and receiving. This breakthrough marks the official entry of commercial aerospace from the "professional field" into the "consumer market". Economic sanctions and technological blockades are forcing China's technological innovation, promoting the miniaturization of satellite terminals and the popularization of communication tariffs, driving the iteration of upstream and downstream technologies in the satellite communication chip and ground signal adaptation industry chain, and providing important market basis for the standardized development of the industry.

Mobile phone directly connected to satellite
07
June 2024: Hainan Commercial Space Launch Site is put into use, improving the "infrastructure" of the entire industry chain
In June 2024, the Hainan Commercial Space Launch Site officially announced that it had the capability to carry out launches. The total budget investment for the project is over 4 billion yuan, equipped with 2 liquid rocket launch stations and 1 solid rocket launch station, and supporting the construction of satellite assembly and testing plants, rocket vertical assembly plants and other full process facilities. Its unique advantages of low latitude, convenient sea transportation, and high launch efficiency are specifically designed to meet the large-scale and high-frequency launch needs of commercial aerospace. The completion and operation of the Hainan launch site has filled the gap in China's lack of commercial space launch sites, marking the completion of the "last piece of the puzzle" in China's commercial space industry chain.

Hainan Commercial Space Launch Site
08
December 2024: intensive networking of dual constellations, China's satellite Internet enters the first year of large-scale construction
At 12:41 on December 5, 2024, the Long March 6A carrier rocket successfully launched the third batch of networked satellites of the "Thousand Sail Constellation" with 15000 satellites planned by Shanghai Yuanxin Satellite into the designated orbit by launching 18 satellites at the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center; At 18:00 on December 16th, the Long March 5B carrier rocket successfully launched the GW low orbit 01 group of 12992 satellites planned by China Satellite Network into the designated orbit at the Wenchang Space Launch Site. Marked by the intensive deployment of the two giant constellations and the entry into the normal launch phase, China's satellite Internet has strided from the conceptual phase to the substantive development phase, entering the "first year" of large-scale construction, bringing practical value to China's provision of satellite Internet commercial services worldwide.
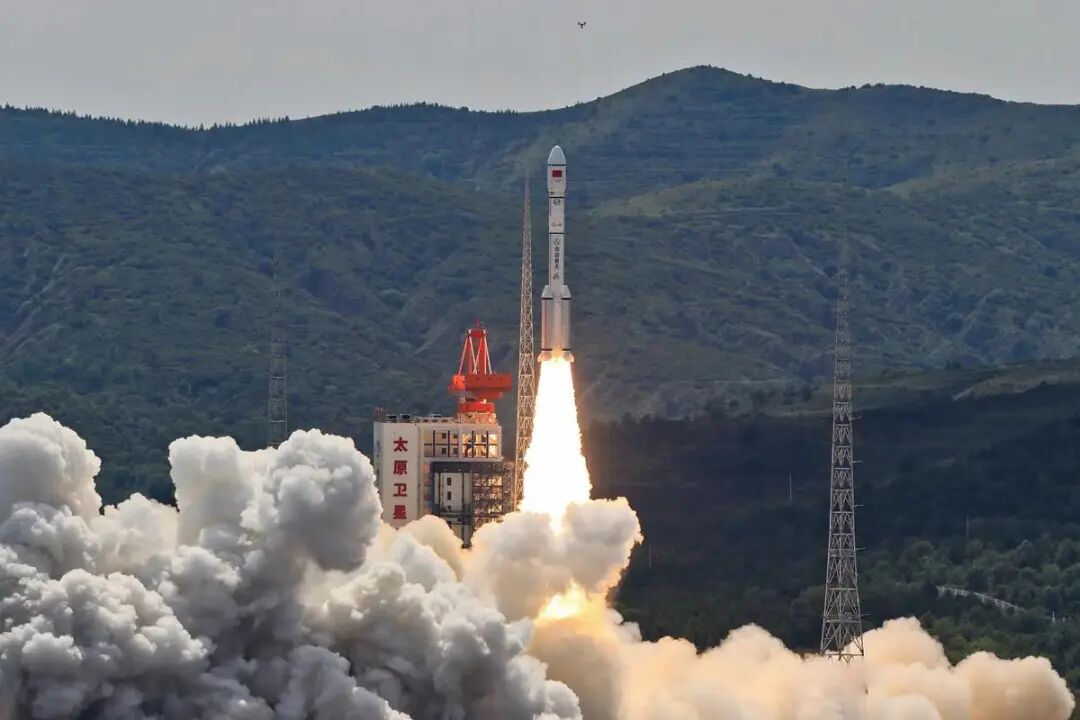

Long March 6A carrier rocket launches' Thousand Sail Constellation '
09
In May 2025, the "Three Body Computing Constellation" will be launched, ushering in a new era of "space+AI"
At 12:12 pm on May 14, 2025, the first batch of 12 computing satellites developed by Zhijiang Laboratory's "Three Body Computing Constellation" were launched into space from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, marking the beginning of the networking phase for the first full orbit interconnected space computing constellation. Its single star has a maximum computing power of 744TOPS, with an overall in orbit computing capability of 5POPS and a storage capacity of 30TB. The satellite is also equipped with an 8-billion parameter space-based model, which can achieve in orbit processing of remote sensing tasks such as classification, interpretation, and detection. Bringing supercomputers into space to achieve "sky computing" has activated a new track of "space+AI", which will drive breakthroughs in the scale of upstream and downstream industries such as satellite data services and space computing power leasing, becoming a landmark event for China to seize the commanding heights of integrated intelligent network technology in the air, space, and earth.

Zhijiang Laboratory releases the "Three Body Calculation Constellation" plan
10
October 2025: Repeatable rockets move towards engineering applications, laying the foundation for the scale of suborbital tourism
From October 18th to 20th, 2025, the Zhuque-3 reusable liquid oxygen methane carrier rocket developed by Blue Arrow Aerospace completed the first phase of its maiden mission at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, including refueling and static ignition tests. All parameters met the design requirements. Zhuque 3 has a low earth orbit carrying capacity of 18 tons (not recovered). The first sub level has the ability of autonomous high-precision return and soft landing, which can support the mission requirements of satellite Internet networking, large communication satellite launch and various types of spacecraft launch. With the continuous breakthroughs in rocket technology, laying the foundation for the large-scale development of suborbital tourism, space travel ticket prices are expected to drop below one million yuan within five years, making the dream of "ordinary people going to space" a reality.

Test footage of Zhuque III reusable liquid oxygen methane carrier rocket
Ten years and a moment, the Milky Way shines brightly. These events outline the evolution trajectory of China's commercial aerospace industry in the first decade: from policy loosening to market driven, from technological catch-up to local leadership, from professional fields to consumer life, it seems that every step has stepped on the rhythm of innovation breakthroughs and industrial landing. After ten years of hard work and breakthroughs, China's commercial aerospace industry has just opened its most exciting chapter. In the remaining month of 2025, TIC believes that there will be breakthrough events in China's commercial aerospace industry. We will continue to enrich this "ten-year history" and this aerospace version of "speed and passion", and wait and see.
In the first decade of China's commercial aerospace industry, what other critical moments illuminated the direction of the future, carried profound significance, and should be recorded and commemorated? Welcome to leave your observations in the comment section.










